Chapter 3 Block Diagrams And Signal Flow Graphs

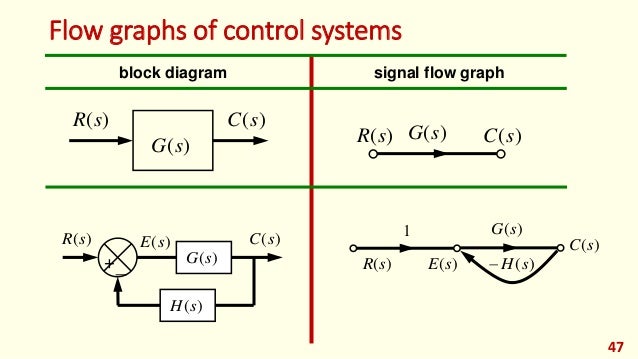
Conversion of block diagrams into signal flow graphs.
Chapter 3 block diagrams and signal flow graphs. To study block diagrams their components and their undlderlying mathematics. Information in chapter 2 we have looked at how to produce a transfer function from differential equations representing a physical system. Block diagram signal flow graphs gate objective numerical type questions question 6 practice book gate ec 1994 iit kharagpur. 5 marks reduce the signal flow graph shown in figure below to obtain another graph which does not contain the node e5.
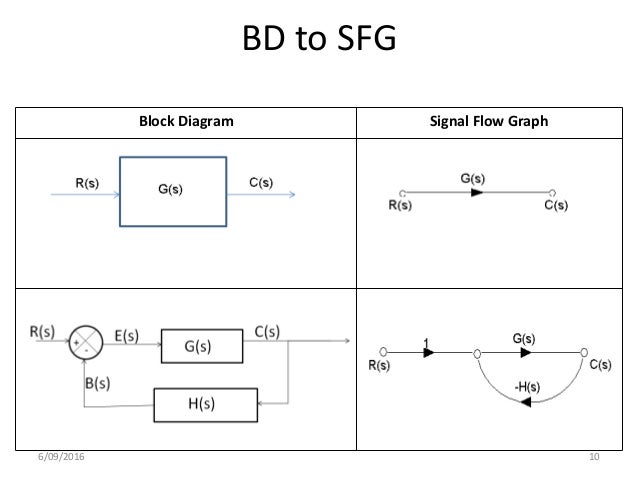
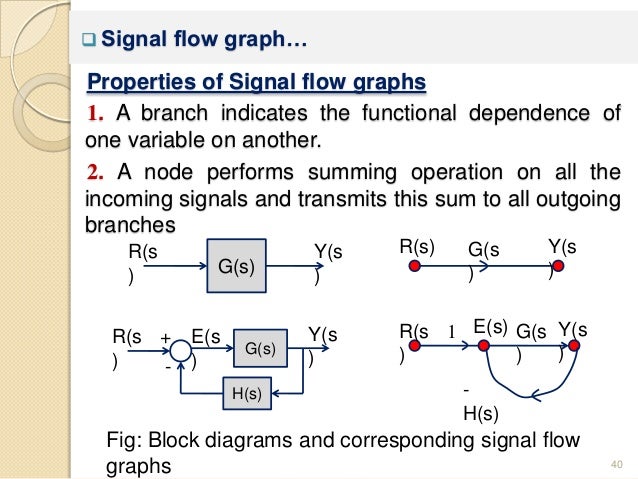
J 1 ra las power amplifier current feedback 2 k u a 4 w i t in 1 j s b tachometer feedback 4 f l gear iuuu a 0 k figure 3p 7 3 8. Also remove any self loop from the resulting graph. For some authors a linear signal flow graph is more constrained than a block diagram in that the sfg rigorously describes linear algebraic equations represented by a directed graph. Represent all the signals variables summing points and take off points of block diagram as nodes in signal flow graph.
To introduce the signal flow graphs. For other authors linear block diagrams and linear signal flow graphs are equivalent ways of depicting a system and either can be used to solve the gain. Objectives of this chapter 1. Follow these steps for converting a block diagram into its equivalent signal flow graph.
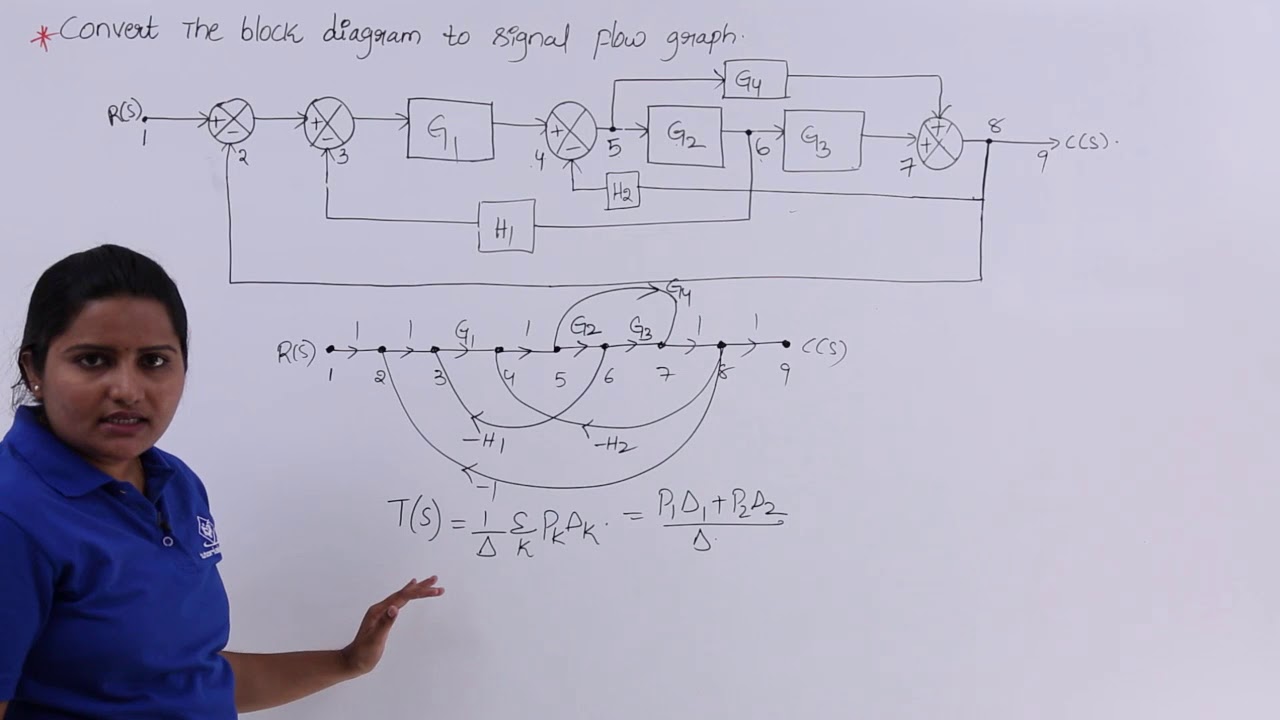
The block diagram of a feedback control system is shown in fig. To obtain transfer function of systems through block diagram maniltiipulation and redtiduction. Step 6 signal flow graph of overall system is shown in the following figure. Find the following.
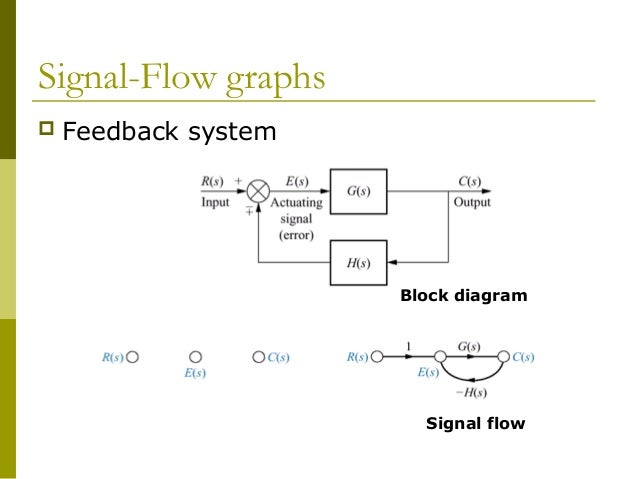
Each component in a control system has a transfer function these components are combined to produce a block diagram we will look at wars to simplify complex block diagrams at the end of this topic chapter 3 you should be able to apply block diagram.